Introduction
Inflammatory Bowel Disease (IBD) is a chronic condition that affects millions of people worldwide. Research conducted by Crohn’s & Colitis UK in 2022 suggests 1 in every 123 people in the UK have either Crohn’s disease or ulcerative colitis. Despite its prevalence, there is still a lack of understanding surrounding this complex condition. In this post, we will delve into the basics of IBD, shedding light on what it is, its symptoms, causes, and available treatment options.
What is Inflammatory Bowel Disease (IBD)? 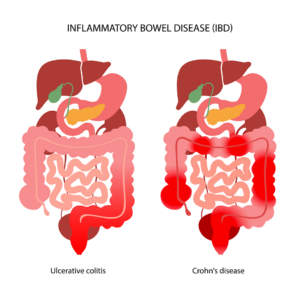
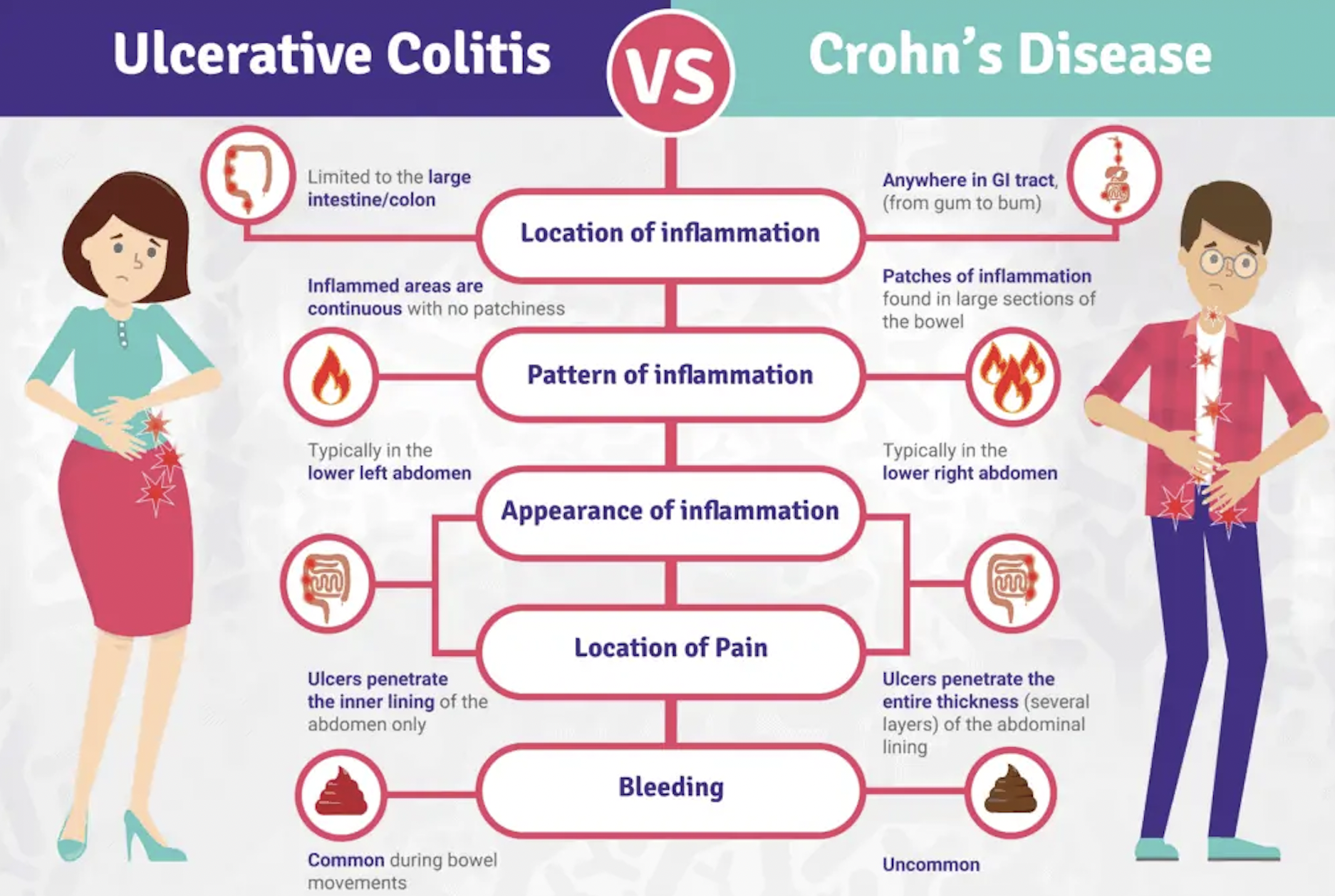
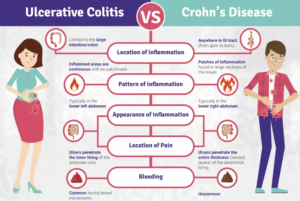
Inflammatory Bowel Disease is a term used to describe a group of disorders characterised by chronic inflammation of the digestive tract. The two primary types of IBD are Crohn’s disease and ulcerative colitis.
- Crohn’s Disease: Crohn’s disease can affect any part of the gastrointestinal tract, from the mouth to the anus. It causes inflammation and damage to the lining of the digestive system, resulting in a range of symptoms such as abdominal pain, diarrhoea, weight loss, and fatigue.
- Ulcerative Colitis: Ulcerative colitis primarily affects the colon and rectum, causing inflammation and ulcers in the inner lining of the large intestine. Common symptoms include abdominal pain, bloody diarrhoea, urgency to have bowel movements, and rectal bleeding.
Causes and Risk Factors
The exact cause of IBD remains unknown, but several factors are believed to contribute to its development:
- Genetics: Family history plays a significant role, as individuals with close relatives who have IBD are at a higher risk.
- Immune System Dysfunction: The immune system mistakenly attacks the healthy cells in the digestive tract, leading to inflammation.
- Environmental Factors: Certain environmental factors, such as diet, smoking, and stress, may trigger or worsen IBD symptoms.
Diagnosis and Treatment
Diagnosing IBD typically involves a combination of medical history, physical examination, laboratory tests, imaging studies, and endoscopic procedures. Gastroenterologists (specialised doctors in digestive disorders) play a crucial role in diagnosing and managing IBD.
Treatment options for IBD aims to control inflammation, reduce symptoms, and improve quality of life. These may include:
- Medications: Anti-inflammatory drugs, immune system suppressors, and biologics are commonly prescribed to manage symptoms and control inflammation.
- Lifestyle Changes: Dietary modifications, stress management techniques, regular exercise, and stopping smoking can help alleviate symptoms and improve overall well-being.
- Surgery: In severe cases or when medications fail to provide relief, surgical intervention may be necessary. Surgical options range from removing a specific segment of the affected intestine to the complete removal of the colon and rectum.
Living with IBD
Living with IBD can be challenging, both physically and emotionally. However, with proper management and support, individuals with IBD can lead fulfilling lives. It is essential to build a strong support network, educate oneself about the condition, and work closely with healthcare professionals to develop a personalised treatment plan.
Conclusion
Inflammatory Bowel Disease is a chronic condition that affects the lives of millions of people worldwide. By understanding the basics of IBD, including its symptoms, causes, and treatment options, we can help create a more supportive and empathetic environment for those living with this condition. Remember, seeking medical advice and support is crucial for effective management and improving the overall quality of life for individuals with IBD.
If you suspect you may have IBD or are experiencing any symptoms, consult with a healthcare professional for a proper evaluation and diagnosis. Together, we can raise awareness, provide support, and enhance the understanding of IBD within our communities.